Resources
Articles
Automate, standardise, and objectively measure your software estate. Understand code quality and the productivity of your developers
Request a Demo Get in Touch
Automate, standardise, and objectively measure your software estate. Understand code quality and the productivity of your developers
Request a Demo Get in Touch
Why we need AI Source Code Detection Tools In the…
Read MoreGetting a good code review process up and running can…
Read MoreDevOps is the combination of software development and operations processes…
Read MoreIn the fast-paced world of software development, Artificial Intelligence (AI)…
Read MoreFor companies serious about optimizing their software estate, measuring and…
Read MoreIn 2024, banks need an objective means of analysing software…
Read MoreThe challenges faced by the banking sector in 2024 mean…
Read MoreThe quest for the most effective metrics to gauge software…
Read MoreIn the rapidly evolving world of software development, the emergence…
Read MoreIntroduction Overview of Current Challenges in Application Development In the…
Read MoreIntroduction In the dynamic world of software development, metrics and…
Read MoreIntroduction In the dynamic world of software development, one of…
Read MoreBeing a Team Lead is both challenging and pivotal within…
Read MoreIn today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, Agile Transformation has…
Read MoreIn recent years, the professional world has experienced a seismic…
Read MoreIntroduction We have been struck by the passionate discussion over…
Read MoreIntroduction Code quality is not just a technical concern; it’s…
Read MoreIntroduction In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, metrics serve as…
Read MoreIntroduction Digital transformation is fundamentally changing businesses by integrating digital…
Read MoreThe Digital Transformation Era’s dawn has radically shifted how businesses…
Read MoreGenerative AI, an AI model designed to generate data similar…
Read More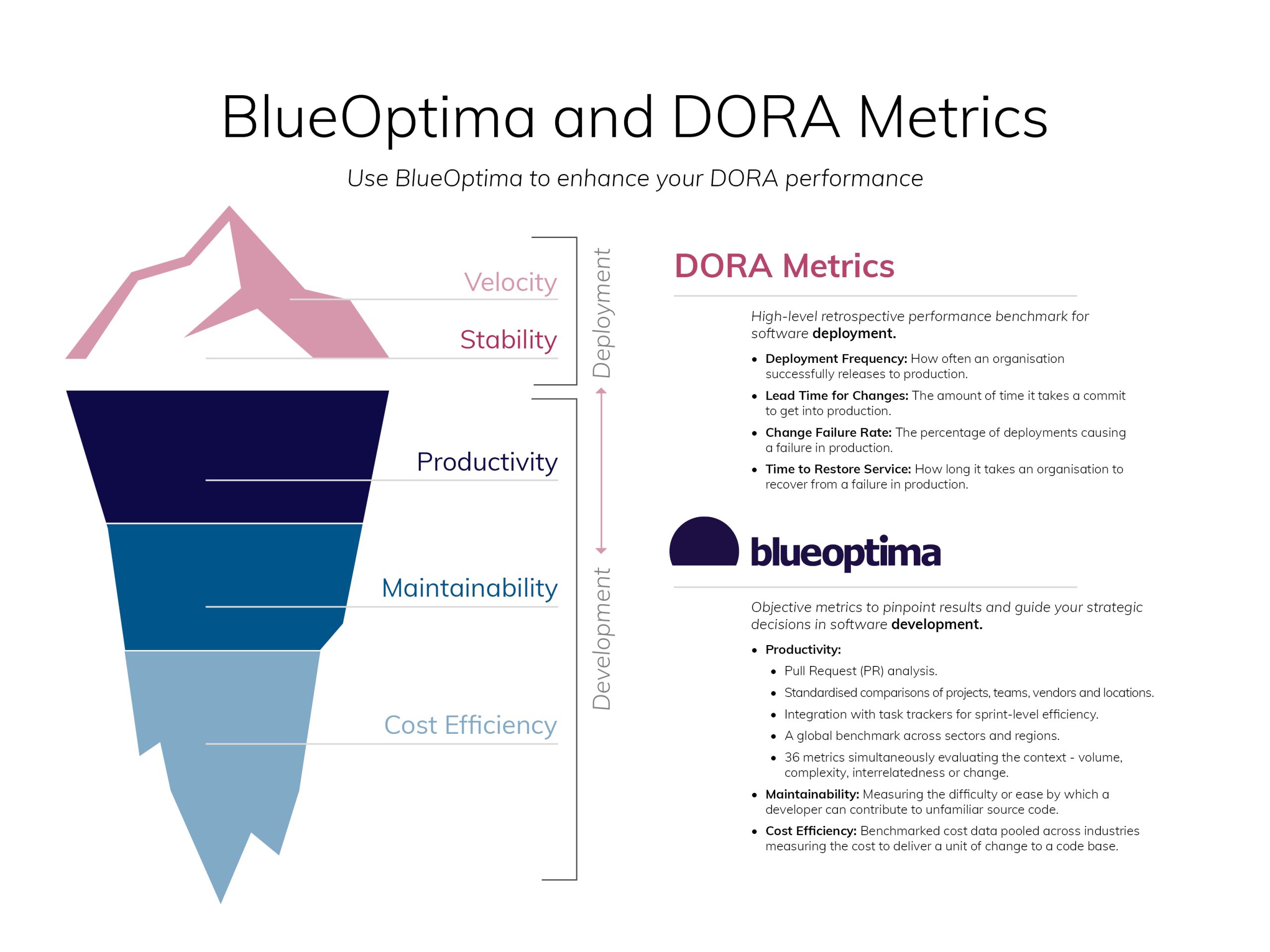
Introduction In the realm of software development, the need for…
Read MoreThe world of software development has introduced numerous frameworks, methodologies,…
Read MoreThe Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) is a systematic process outlining…
Read MoreCyclomatic complexity is a crucial metric for measuring the complexity…
Read MoreCyclomatic complexity is a popular metric for measuring code quality….
Read MoreCyclomatic complexity is an essential metric that measures the complexity…
Read MoreCyclomatic complexity is a metric used to measure the complexity…
Read MoreThe integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)…
Read MoreFor every aspiring software developer, the concept of ‘code quality’…
Read MoreFunction points are one of the most commonly used measures…
Read MoreIf you’re in the talent acquisition field, you know that…
Read MoreDORA is a widely used framework for measuring performance, but…
Read MoreIn today’s economy, retaining software developers is more important than…
Read MoreDoes your team ever hit a point where you’re working…
Read MoreDigital transformation is a must for any company looking to…
Read MoreAs technology evolves, more and more companies are turning to…
Read MoreIn computer systems engineering and management, Mean Time To Repair…
Read More
Understand more about software development with this infographic.
Read More
When did you join BlueOptima? I joined in January 2018…
Read MoreThe success of software development projects largely depends on effective…
Read More
Every company that sells software as a product or relies…
Read More
Communication within software development teams is vital, more than it…
Read More
A 2021 study by Stepsize showed that although 60% of software…
Read More
Productivity is difficult to measure from an external perspective. For…
Read MoreCode complexity measures how difficult it is to understand, modify,…
Read More
Software development, and the tech industry as a whole, have…
Read MoreThe software industry — particularly the game development sector —…
Read MoreIn today’s fast-paced and competitive technology landscape, measuring developer productivity…
Read MoreShifting left is not a cutting-edge concept within software development….
Read MoreAgile vs Waterfall, what’s the fuss? Whenever you create a…
Read MoreHow has COVID-19 impacted your developers? 80% of software developers…
Read MoreToday, undertaking some form of digital transformation is inevitable. Technological…
Read MoreDigital transformation is high on the agenda for many companies,…
Read MoreDid you know that businesses which prioritised cross-functional considerations were twice…
Read MoreAccording to research carried out by BCG, a staggering 70% of digital transformation…
Read MoreDigital transformation is an essential part of modern business. Companies…
Read MoreLooking to improve the productivity of your development teams? Which…
Read MoreThe BlueOptima Global Benchmark Report shows that software development productivity…
Read MoreThe BlueOptima Global Benchmark Q4 2022 report has highlighted a growing trend:…
Read MoreEastern Europe is becoming an increasingly major competitor in the…
Read MoreAs we look back at the developer population data collected…
Read MoreThe UK technology sector has a rich history of innovation…
Read MoreAs famous management consultant Peter Drucker once said, “if you…
Read MoreEquipped with a complex range of skills, software developers who…
Read MoreThe software development landscape is changing rapidly, and the demand…
Read MoreA lack of diversity can limit an organisation’s innovation. Therefore,…
Read MoreOrganisations wanting to improve their software development capacity are having…
Read MoreThe 10x developer who is 10 times more productive than…
Read MoreTo get more out of software development, organisations must create…
Read MoreGiven the vast sums of money organisations invest in software…
Read MoreIn a broad sense, there are several aspects of software…
Read MoreBlueOptima offers a solution to a long-standing problem that hitherto…
Read MoreIntroduction This is a series of blog posts that respond…
Read More
Giving teams visibility, managers are enabled to increase the velocity of development teams without risking code quality.
out of 10 of the worlds biggest banks
of the S&P Top 50 Companies
of the Fortune 50 Companies